- Home
- Up to XII Students
- Decide Stream For XI & XII
- Career Options
- Entrance Preparation
- Sample Papers
- Entrance Exams after 12th
- International Entrance Exams To Study Abroad
- Foreign University Comparison
- Apply to Foreign Universities
- General Preparation For Students Going To Study Abroad
- Write A Report
- Write an Article
- Write An Essay
- Important Dates
- UG & PG
- Tech Tips
- Mock Test
- GROOMING
- HOBBIES
- K PLUS
- Working Professional
- OTHERS
ROLE OF ELECTRICAL VEHICLES WITH MICROGRD IN SVING CLIMATE AND ITS ADVANTAGES
Shailesh M. Deshmukh
Assistant Professor & HOD
Department of Electrical Engineering
Kalinga University, Naya Raipur (C.G)
Shailesh.deshmukh@kalingauniversity.ac.in
Electric energy is a requirement because the modern way of life of humanity depends on its usage [1]. An ever-increasing need for energy has been caused by the growing population. Most of the total demand for power is satisfied through conventional sources, which are constantly running out and posing major environmental risks [1]. Additionally, the urbanisation and smart city sectors are expanding quickly, contributing to the apex of the transportation era. As a result, the number of conventional cars on the road is increasing, which contributes significantly to greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Figure 1 depicts the rising CO2 trend from several sources of exploitation. Compared to the industrial, residential, and commercial sectors, the transportation sector has a greater slope (i.e., a higher rate of CO2 increase)
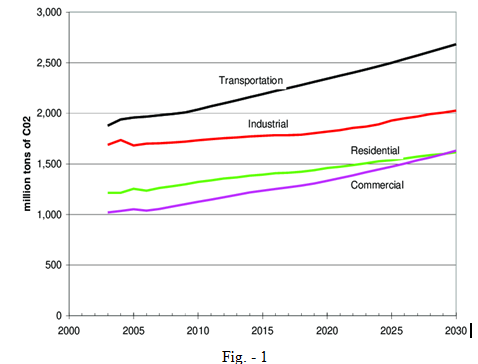
Fig. – 1
Thus, it can be claimed that the
urban communities are growing increasingly concerned about the rising
atmospheric adulteration caused by the exponential rise of urbanisation,
industrialization, and an increase in the number of on-road vehicles. Distributed
generation (DG) and transportation systems based on alternative fuels must be
immediately implemented in order to combat this growing problem.
Microgrid-based charging stations are receiving a lot of attention in this area
[3].
Incorporating a well-defined electric vehicle
charging infrastructure into the smart grid can present a number of
opportunities, especially from the standpoint of vehicle-to-grid (V2G)
technology and as a way to address the intermittent nature of renewable energy
[3].
Advantages
1.
Low running costs.
2.
Low Maintenance Expenses.
3.
No Tailpipe Emission.
4.
Tax and Financial Benefits.
5.
Clean and Green Environment.
6.
Reduce Energy Lost.
7.
Noise pollution free.
References:-
[1] M. Asaad, F. Ahmad, M. S. Alam, and G.
Das, “Automation of the grid: Indian
initiatives,” in Proceedings of 2017 IEEE
International Conference on Technological
Advancements in Power and Energy (TAP Energy), 2018,
pp. 1–5.
[2] U.S. Energy Information Administration,
“Annual Energy Outlook 2009, With
Projections to 2030,” Outlook, vol. 0383, no. March,
p. 221, 2009.
[3] W. Khan, A. Ahmad, F. Ahmad, and M. Saad
Alam, “A Comprehensive Review of Fast
Charging Infrastructure for Electric Vehicles,” Smart
Sci., vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 1–15, 2018

Kalinga Plus is an initiative by Kalinga University, Raipur. The main objective of this to disseminate knowledge and guide students & working professionals.
This platform will guide pre – post university level students.
Pre University Level – IX –XII grade students when they decide streams and choose their career
Post University level – when A student joins corporate & needs to handle the workplace challenges effectively.
We are hopeful that you will find lot of knowledgeable & interesting information here.
Happy surfing!!
- →
-
Free Counseling!
